Jan 16th, 2024: ZeroFlow was accepted to ICLR 2024!
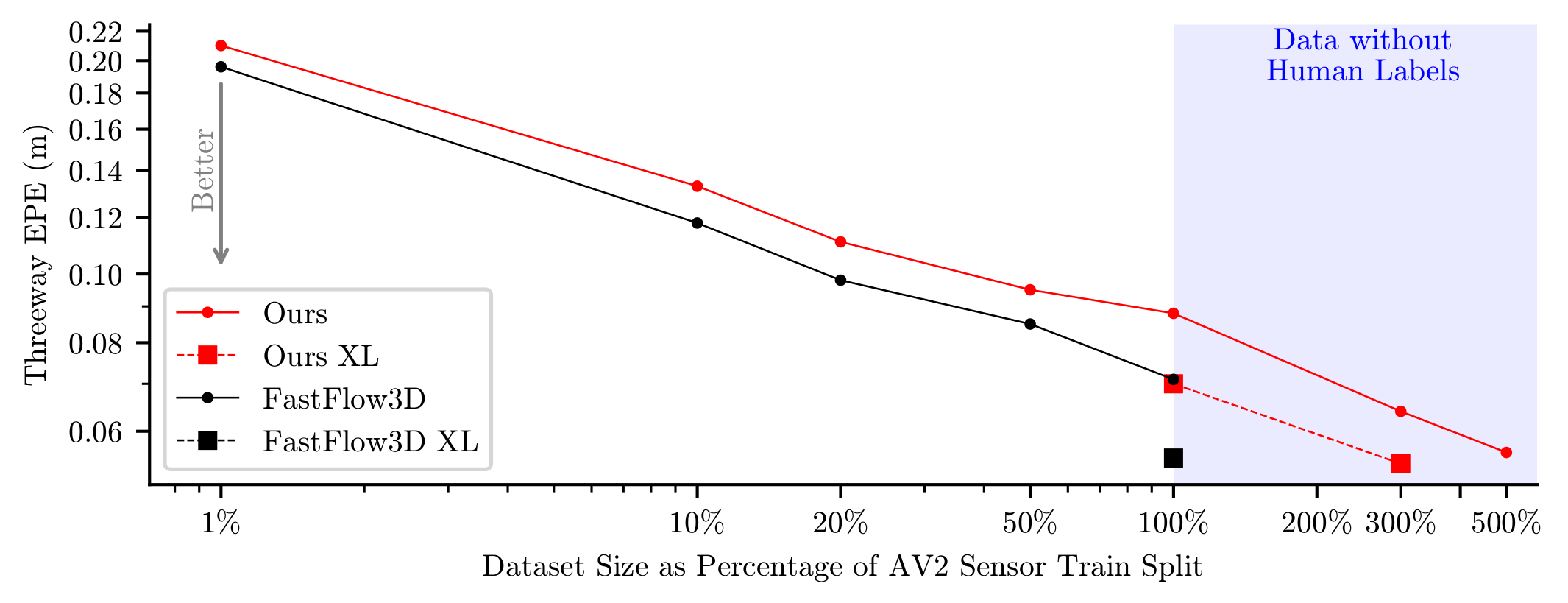
Jul 28th, 2023: We scaled up the ZeroFlow pipeline on additional point clouds from the unlabeled Argoverse 2 LiDAR dataset. With 3x the data, we beat the supervised baseline and teacher performance; with 3x the data and a bigger backbone, we are state-of-the-art on the Argoverse 2 Self-Supervised Scene Flow Leaderboard! Scaling ZeroFlow on raw data logs is all you need to build state-of-the-art scene flow methods — AV companies should try this on their internal logs!
Jun 18th, 2023: ZeroFlow was selected as a highlighted method in the CVPR 2023 Workshop on Autonomous Driving Scene Flow Challenge!
Scene flow estimation is the task of describing the 3D motion field
between temporally successive point clouds. State-of-the-art methods use
strong priors and test-time optimization techniques, but require on the
order of tens of seconds to process large-scale point clouds, making
them unusable as computer vision primitives for real-time applications
such as open world object detection. Feed forward methods are
considerably faster, running on the order of tens to hundreds of
milliseconds for large-scale point clouds, but require expensive human
supervision. To address both limitations, we propose Scene Flow via
Distillation, a simple, scalable distillation framework that uses a
label-free optimization method to produce pseudo-labels to supervise a
feed forward model. Our instantiation of this framework,
ZeroFlow, achieves state-of-the-art
performance on the Argoverse 2 Self-Supervised Scene Flow
Challenge while using zero human labels by simply training on
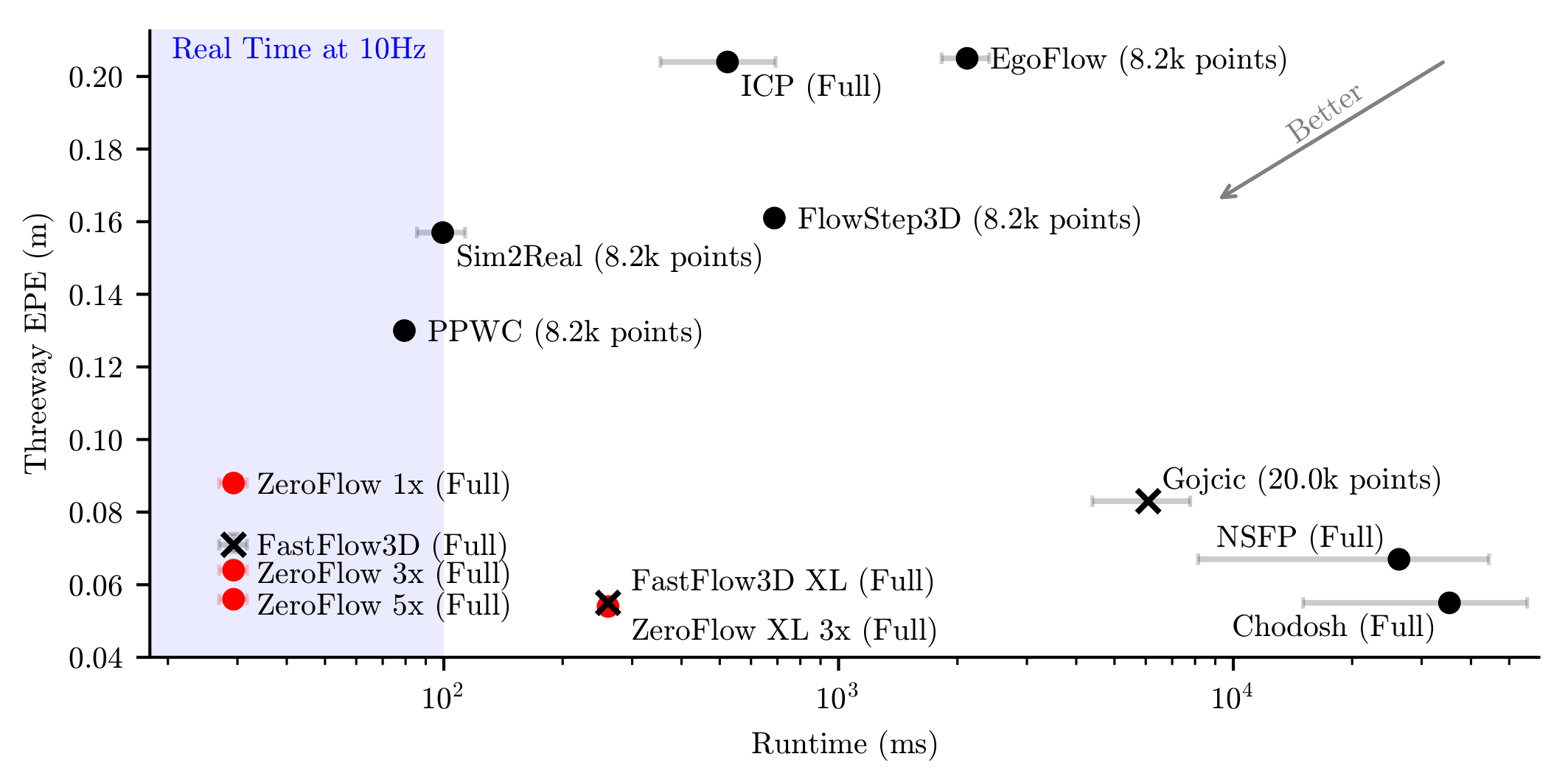
large-scale, diverse unlabeled data. At test-time, ZeroFlow is over
1000![]() faster than
label-free state-of-the-art optimization-based methods on large-scale
point clouds and over 1000
faster than
label-free state-of-the-art optimization-based methods on large-scale
point clouds and over 1000![]() cheaper to train on
unlabeled data compared to the cost of human annotation. To facilitate
further research, we will release our code, trained model weights, and
high quality pseudo-labels for the Argoverse 2 and Waymo Open
datasets.
cheaper to train on
unlabeled data compared to the cost of human annotation. To facilitate
further research, we will release our code, trained model weights, and
high quality pseudo-labels for the Argoverse 2 and Waymo Open
datasets.
Existing scene flow estimation methods are either slow but label free test-time optimization methods, or fast but human supervised feed forward networks. We construct the Scene Flow via Distillation framework to break this tradeoff.
Our straight-forward instantiation of this in ZeroFlow shows that simply training a supervised model with imperfect pseudo-labels can exceed the performance of perfect human labels on substantial fraction of the data. We think this is itself surprising, but we also think it has highly impactful implications for the problem of scene flow estimation: point cloud quantity and diversity is more important than perfect flow label quality for training feed forward scene flow estimators.
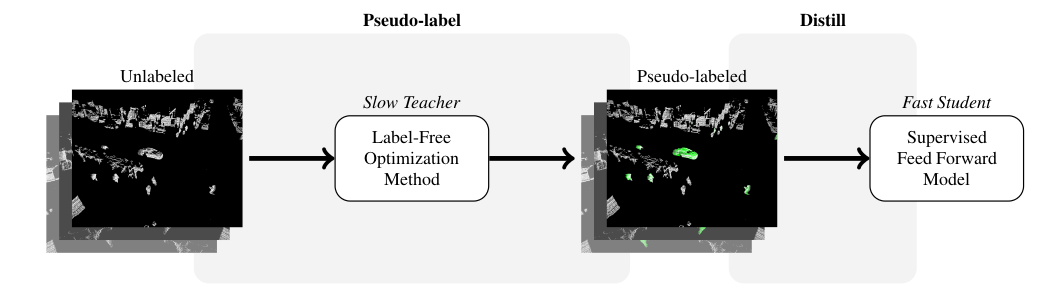
We instantiate this framework in ZeroFlow, a scene flow method that scales to real world point clouds. ZeroFlow uses Neural Scene Flow Prior, a high quality label-free optimization method, to generate pseudolabels to train FastFlow3D, a fast, scalable feed forward scene flow network. The resulting method is real-time and produces state-of-the-art quality flows with zero human labels.
@inproceedings{vedder2024zeroflow,
author = {Vedder, Kyle and Peri, Neehar and Chodosh, Nathaniel and Khatri, Ishan and Eaton, Eric and Jayaraman, Dinesh and Liu, Yang and Ramanan, Deva and Hays, James},
title = {{ZeroFlow: Scalable Scene Flow via Distillation}},
journal = {Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR)},
year = {2024},
website = {http://vedder.io/zeroflow.html},
pdf = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2305.10424.pdf}
}